Myopia Control and Prevention
M3 India Newsdesk Jan 03, 2025
This article provides an in-depth overview of myopia discussing its causes, types, symptoms, and prevalence. It highlights the global public health impact of myopia and its increasing prevalence, particularly in the post-COVID era.
Myopia is the most common refractive error among the youth. It is also known as shortsightedness, where the light rays coming from distant objects focus slightly anterior to the retina, resulting in the blurring of images of distant objects.
Nearby objects can still be seen clearly, however; that is why it is termed as shortsightedness.
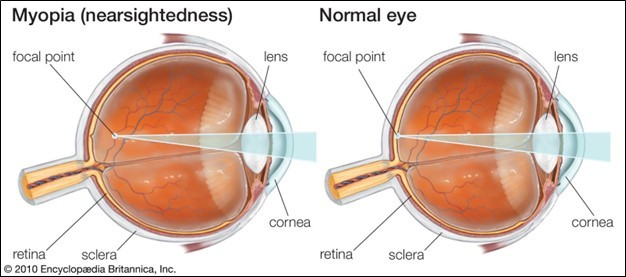
Varying mechanisms of myopia
1. Axial myopia is attributed to an increase in the axial length of eyeballs.
2. Refractive myopia is attributed to the condition of the refractive elements of the eye. It can be further subclassified into :
- Curvature myopia is attributed to an increase in the curvature of the cornea and/or lens causing high corneal and lenticular power as in: Keratoconus (increase in corneal curvature), Lenticonus (increase in curvature of Lens ); it also presents itself in two further subtypes - Anterior Lenticonus and Posterior Lenticonus.
- Index myopia is attributed to variation in the index of refraction of one or more ocular media, i.e. Aqueous Humour and Vitreous Humour.
3. Psuedomyopia is attributed to excessive accommodation of the eye during a prolonged duration of work involving strain on the eyes.
4. Acquired myopia is attributed to high blood glucose levels leading to swelling of the lens, which causes myopic effect. It can also occur due to certain drugs (such as Acetazolamide and Topiramate) leading to ciliary body effusion which causes myopia.
Symptoms of myopia
- Blurred vision, especially for distance
- Headache
- Eye strain
Very young patients may be asymptomatic and may be diagnosed during routine screening.
Classification of myopia

Prevalence
Myopia is a common refractive error and an important cause of Ocular Morbidity, especially in the younger generation. It has evolved into a major public health problem globally; the American Academy Of Ophthalmology predicts that nearly 50% of the world population will be myopic by 2050. Uncorrected myopia can have a huge social, psychological, economic and developmental impact. It can also cause degenerative changes in the retina and optic disc and may lead to sight-threatening sequalae.
Point prevalence in population at any point in time among all age groups and all regions is difficult to ascertain and it varies in different studies owing to variations in age groups, region and certain other factors. Population-based surveys have documented incidence between 3.6% to 36.5%. The prevalence of myopia in the results of hospital-based studies and school-based studies is approximately 8.5% to 9%. As per prevalent literature prevalence of myopia in society in 1999 was 8.59 %, a figure that has now reached up to 23%-30% in the post-COVID era.
Quality of life suffers greatly in myopia; this takes place in the form of poor academic performance, restriction in sports, social stigma due to spectacles etc.
Comorbidities associated with Myopia patients are Glaucoma, Cataract, Chorioretinal Degeneration, CNVM, Macular hole, Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment, Strabismus and Amblyopia.
Predisposing factors
- Hereditary and genetics: 18 different loci on 15 chromosomes have been identified, but their exact relation and mutation is still not defined and under research.
- Environmental factor: The risk of myopia increases with insufficient light exposure, low physical activity, near work, and increased years of education.
One hypothesis is that a lack of normal visual stimuli causes improper development of the eyeball. Nowadays, as the majority of individuals spend most of their time indoors in dimly or fluorescently lit buildings, they are at risk of developing myopia.
People, and children especially, who spend more time in physical exercise and outdoor playing have lower rates of myopia. It has been suggested that increased magnitude and complexity of the visual stimuli encountered during the above activities decrease myopic progression. There are documentary evidence that the development of myopia is delayed by long hours of exposure to daylight as it impacts the production and release of retinal dopamine which inhibits the axial growth of the eye.
Minus spherical lenses can induce myopia and overcorrected minus prescription lenses may lead to myopia progression. Overcorrection of minus lenses during refraction can be avoided through various techniques and tests, such as fogging and duo-chrome test.
The near-work hypothesis also referred to as the "use-abuse theory", states that spending time involved in near-work strains the intraocular and extraocular muscles.
Other associations of myopia include:
- Diabetes
- Childhood Arthritis
- Uveitis
- Systemic Lupus Erythematous
Complications of myopia
- Dependency on spectacles for normal vision
- Retinal degeneration
- the eye becomes predisposed to retinal tears (excessive axial growth causing elongation of eyeball stretching and thinning of sclera choroid and retina)
- Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment
- Macular hole
- Early cataract
- POAG (Primary Open Angle Glaucoma)
- Constriction of visual field and night blindness
- Squint
Prevention of myopia
Hereditary and genetic factors cannot be modified, but we can modify environmental factors. One of the major ways to do this is by promoting more outdoor activities and involvement in sports. Another preventive measure is good illumination and lighting while working indoors.
Myth 1: Exercise can revert myopia.
Fact: Exercise cannot cure myopia, but orthoptic exercise can correct convergence weakness.
Myth 2: Herbal eye drops can help in removing glasses.
Fact: Eye drops cannot remove glasses, but according to newer studies, Low-dose atropine can help in controlling the progression of myopia.
Management of myopia
1. Glasses: For younger subsets glasses are the mainstay of therapeutic options for myopia.
2. Contact Lenses: Contact lemyopianses are a good alternative but we need to maintain it carefully and keep it hygienically as there may be the risk of corneal infection with Contact lenses if not used hygienically.
3. Refractive Surgeries: Post eighteen years of age and post-stabilisation of refractive error, various refractive surgeries can be offered for myopia. Depending upon refractive error and corneal topography map evaluation for corneal thickness, we have several options available as per grading of Myopia,
- LASIK(Laser-assisted in situ keratomileusis)
It is a technique wherein a microkeratome / handsome-assisted corneal flap is made and the underlying stroma is ablated by Excimer laser to reshape the corneal stroma as per the refractive error of the patient.
Limitation: Residual corneal thickness should be 250 to 300 microns as otherwise complications like Ectasia and recurrence of refractive error will be there hence it is appropriate only for Mild to moderate myopia.
- EPI- Lasik
Here a corneal flap is made by an epikeratome ( epithelium Separator) which is thinner than the flap of Lasik and it doesn’t create a vacuum and is appropriate for glaucoma subsets. Hence it is good in subsets having cornea with less thickness.
Limitation: as above
- PRK
Here Superficial corneal epithelium is removed and then Excimer laser is applied over the corneal stroma.
Limitation: Post-op Pain and discomfort will be there owing to epithelium ablation and it takes 48 hrs. for epithelium to Completely regenerate.
- FEMTO LASIK
The corneal flap is made by Femto laser which places a spot on the cornea till the required depth and then the flap is removed before the excimer laser
- LASEK
Here the epithelium layer is rolled up by using alcohol and replaced back after the Excimer laser procedure In PRK epithelium is removed completely but here a flap of epithelium is made by using alcohol and is rolled back after the Laser, so post-op discomfort will be less after the procedure.
Limitation: since alcohol is epitheliotoxic post-operation recovery time increases.
- SMILE (small incision lenticule extraction)
- SILK (smooth incision lenticule keratomileusis )
These are flapless procedures where a Femto Laser flap of adequate thickness is created inside the stroma and a lenticular is removed with the help of micro forceps and lenticular stripper.
More recent advances available are:
- Clear lens extraction with IOL implantation
This is an intraocular process but it should be avoided in very young individuals as complications like RD, vitreous loss and Contrast problems are known to occur.
- Phakic IOL
ICL (implantable collamer lens / CAIRS Corneal allogenic Intrastromal ring segments ) are available and can be inserted into the eye over a normal natural lens. The Prerequisites include an anterior chamber depth of more than 2.8 mm and angle closure glaucoma or uveitis are ruled out prior to the procedure.
Control of myopia
To prevent the rapid progression of myopia at a young age the following options are available:
- Environmental control
Greater outdoor activity, good exposure to light, good diet.
- Pharmacological control
ATOM study revealed the effectiveness of low-dose atropine (0.5%, 1% and .01% )administration at nighttime only, in children below 16 years of age which helps in reduction in myopi progression. The efficacy of all of the above remains equal.
- Orthokeratology
It assists with the reduction, modification/elimination of corneal refractive error with a programmed contact lens application. Here we use RGP ( as per the base curve of the cornea) to induce corneal surface changes from prolate to ablate by overnight wearing of RGP lenses and it can temporarily flatten the corneal surface during daytime for 5 /6 hours and eliminate the use of spectacles for daytime. It is extremely expensive and hygiene-related issues, especially with young children need to be addressed.
Newer technology
- Multifocal contact lens
Glasses based on the peripheral myopic defocusing principal:
These glasses have central focusing power, but in the periphery, defocusing elements are present in different shapes and patterns creating a myopic defocus. This forces the retina to move forward which prevents the progression of refractive error.
The types of glasses include:
- DIMS
- HALT
- CARE
- Dots
However, cost remains a limiting factor.
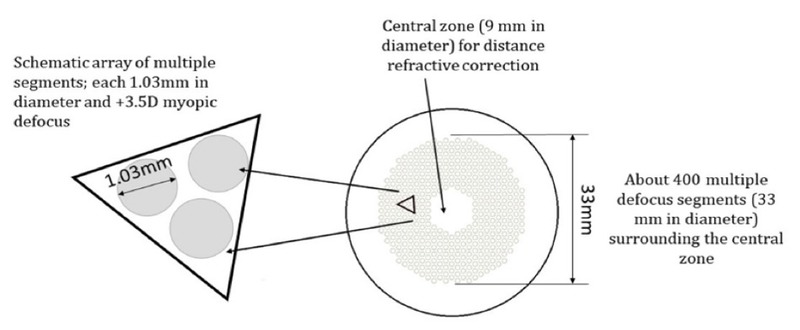
Figure 1: The design of the Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments (DIMS) spectacle lens.
-
Colour therapy
Violet light may prevent myopia progression, but a definitive role is not established in the currently available literature.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr. Vandana Jain is a Senior Consultant at ESIC Hospital, Indore.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries