Comprehensive Management Guidance for Diarrhoea and Vomiting
M3 India Newsdesk Jan 27, 2023
Vomiting and diarrhoea are frequent signs and symptoms of numerous ailments. Infection is typically the cause of these symptoms, which can affect both adults and children hence how to treat diarrhoea and vomiting is explained in this article.
Diarrhoea is defined as the occurrence of three or more loose or watery stools per day (or more frequent passage than normal for the person). The most characteristic feature of diarrhoea is a recent change in stool consistency. It can result in dehydration which is the most dreaded complication.
Prevalence
Diarrhoea is the second most common cause of death in children below five years of age and is the major cause of malnutrition in this age group. The mortality rate due to diarrhoeal disease in India is approximately 13% in children under five age group. The incidence of diarrhoeal disease is maximum in summer followed by rainy or winter seasons. Diarrhoeal diseases are preventable and can be treated effectively.
Causalities
The commonest cause of vomiting and diarrhoea is an infection caused by microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites. The mode of transmission is by the faecal-oral route due to faecal contamination of water and food. The absence of sanitation and hygiene and the lack of safe water is responsible for the spread of the disease. The common etiological agents include Rotavirus and Escherichia coli. Malnutrition in children increases the susceptibility to diarrhoeal diseases which in turn worsens malnutrition. Person-to-person transmission can occur due to poor personal hygiene. Diarrhoea commonly stops within 5-7 days and vomiting generally stops in 1-2 days. Reactions to drugs, allergy or intolerance to certain foods, and intestinal disorders are other causes of vomiting and diarrhoea.
Management
The hallmark of the management of diarrhoea and vomiting is to prevent and manage dehydration since there is a loss of water and electrolytes from the body which needs to be promptly corrected. Oral rehydration solution (ORS) containing glucose and electrolytes in a specific ratio to replace the water and electrolytes lost due to vomiting and diarrhoea is the mainstay of management. ORS is safe and the preparation is simple.
1. The preparation and administration of ORS are as follows:
- One packet of ORS is usually meant to make 1 L of solution and the entire packet has to be prepared. Incomplete preparation should be avoided. Also, readymade liquid preparations of ORS may not have the recommended composition of electrolytes and sugar and should be avoided.
- ORS should be given after every loose stool in the dosage given in the table.
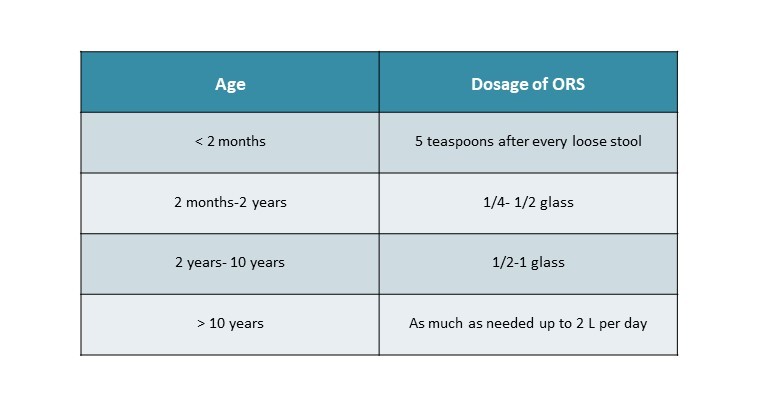 A dosage of ORS as per age
A dosage of ORS as per age
- ORS should be given very slowly in small sips rather than rapidly with a glass since rapid consumption can cause vomiting.
- After preparation, the ORS can be used for 24 hours after which it has to be discarded and fresh preparation should be done.
2. The following food and drinks should be avoided:
- Carbonated drinks, fruit drinks, fruit juices, and plain glucose solutions
- Caffeinated drinks like tea, coffee
- Processed food
3. Other liquid diets:
Vomiting and diarrhoea are generally self-limiting and resolve within 3-7 days.
- It is recommended that apart from ORS, infants should also continue to receive breast milk.
- For children and adults, along with ORS other fluids which can be given are:
- Rice or pulse-based drink
- Vegetable soup
- Coconut water
- Yoghurt drink
- Lemon drink
- Plain water
4. Zinc supplementation: It is recommended for diarrhoea and vomiting for not only a reduction in severity and duration of diarrhoea but also for the prevention of further episodes for at least the next 3 months.
The dosage is:
- For children between 6 months to 5 years - 20 mg/day for 14 days
- For children between 2-6 months -10 mg/day for 14 days
5. Antibiotics: These are generally not required even in bacterial infections since most infections are self-limiting. Antibiotics are recommended in the following conditions:
- Blood in stool
- Some other concomitant infections (e.g., pneumonia, ear infection, and urine infection)
- Severe malnutrition or immunodeficiency states.
6. Dehydration: Patients and caregivers should be educated to look out for warning signs of dehydration such as:
- Reduced frequency or quantity of urine
- Feeling very thirsty or restless
- Looking more ill
- Vomiting everything
- Blood in stool
- Inability to drink or breastfeed
- Cold extremities
- Change in responsiveness (drowsy or lethargy)
Vomiting can be controlled by eating light and bland food, avoiding sweet, oily and greasy food, eating slowly and small frequent meals, and avoiding activity and teeth brushing after eating and drinking fluids slowly.
Persistent diarrhoea
The presence of diarrhoea for more than 2 weeks is known as persistent diarrhoea occurring in 10% of the patients.
The following can be the causes of persistent diarrhoea:
- Persistence of infection
- Excessive juice or carbohydrate-sweetened liquid consumption
- Medication
- Altered immune function
- Allergies or intolerance to certain foodstuffs
Management of persistent diarrhoea is to treat the cause.
Prevention
The following measures can be advised for the prevention of diarrhoea and vomiting:
- Proper nutrition: Adequate nutrition can prevent recurrent infections
- Ensuring patient compliance to complete the 14-day course of zinc supplementation
- Adequate personal and food hygiene such as frequent hand washing, consumption of safe water and food
- Vaccination against rotavirus and measles
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author's and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Mohini Gore is a PhD and MBBS from Bangalore.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries