Androgenetic Alopecia in Men & Women: Effective Treatment Options
M3 India Newsdesk Jul 05, 2023
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common form of hair loss in both men and women. This article explains the various stages of AGA in men and women along with its management.
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA)
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, and results in the progressive miniaturisation and eventual loss of hair follicles. AGA can affect people of any age, but it is most common in adults between the ages of 20 and 50.
In men, AGA typically manifests as a receding hairline and thinning of hair on the crown of the head. The hair loss may be symmetrical, or it may be more pronounced on one side of the head. In some cases, men with AGA may develop a bald spot on the crown of the head.
In women, AGA is more likely to cause diffuse thinning of hair across the scalp. The hair loss may be more noticeable at the temples and crown, but it is less likely to lead to complete baldness.
Treatment
There is no cure for AGA, but there are a number of treatments that can help to slow the progression of hair loss and promote regrowth. The most common treatments for AGA include:
- Minoxidil: A topical medication that can be applied to the scalp twice daily. Minoxidil works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, which can help to stimulate hair growth.
- Finasteride: A oral medication that can be taken once daily. Finasteride works by blocking the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is a hormone that is thought to play a role in AGA.
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy: A procedure in which a small amount of blood is drawn from the patient and then processed to separate the platelets. The platelets are then injected into the scalp, where they release growth factors that can help to stimulate hair growth.
- Hair transplantation: A surgical procedure in which hair follicles are removed from a donor area of the scalp and transplanted to the balding area.
The choice of treatment for AGA will depend on the severity of the hair loss, the patient's age and overall health, and their personal preferences.
Stages of AGA
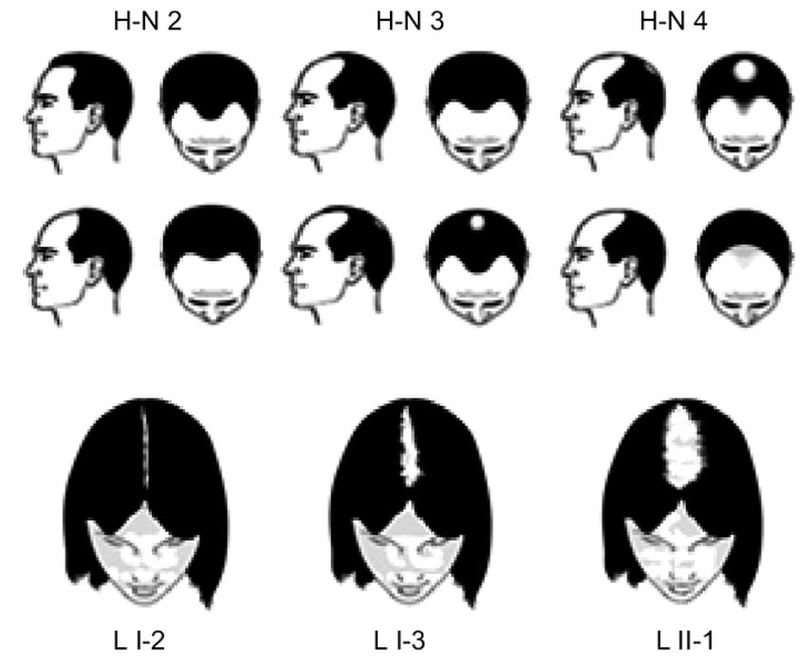
The stages of AGA in men are classified using the Norwood scale, which ranges from Stage 1 (little or no hair loss) to Stage 7 (complete baldness). The stages of AGA in women are classified using the Ludwig scale, which ranges from Stage I (little or no hair loss) to Stage III (noticeable hair loss).
Here is a summary of the stages of AGA in men and women:
Men
- Stage 1: There is little or no hair loss.
- Stage 2: There is slight hair loss near the temples.
- Stage 3: The hairline recedes further and may start to resemble an "M" shape when viewed from above.
- Stage 4: There is significant hair loss. The hairline recedes farther and may start to resemble a "U" shape when viewed from above. The bald spot on the crown is larger, but there is still a strip of hair between the bald spot and the receding hairline.
- Stage 5: The hairline recedes to the point where there is only a small strip of hair around the sides and back of the head.
- Stage 6: The hair on the sides and back of the head also starts to thin and fall out.
- Stage 7: Complete baldness.
Women
- Stage I: There is little or no hair loss.
- Stage II: There is a widening of the part in the hair, with some thinning of hair on the crown.
- Stage III: The hair on the crown becomes more noticeably thin.
- Stage IV: The hair on the crown becomes very thin, and there may be some hair loss at the temples.
- Stage V: The hair on the crown is almost completely gone.
It is important to note that the stages of AGA can vary from person to person. Some people may progress through the stages more quickly than others. There is no cure for AGA, but there are treatments that can help to slow down hair loss and promote hair growth.
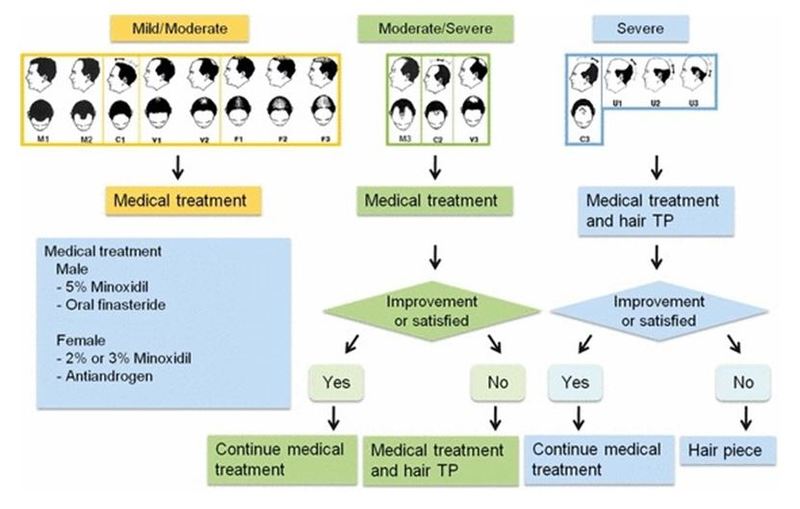
Treatment depends upon the stage
The treatment options for androgenetic alopecia (AGA) in men and women vary depending on the stage of hair loss.
Men
- Norwood Stage 1: There is little or no hair loss. Treatment is usually not necessary at this stage.
- Norwood Stage 2: There is slight hair loss near the temples. Treatment options include topical minoxidil and oral finasteride.
- Norwood Stage 3: The hairline recedes further and may start to resemble an "M" shape when viewed from above. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, and low-level laser therapy (LLLT).
- Norwood Stage 4: There is significant hair loss. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, LLLT, and hair transplantation.
- Norwood Stage 5: The hairline recedes to the point where there is only a small strip of hair around the sides and back of the head. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, LLLT, and hair transplantation.
- Norwood Stage 6: The hair on the sides and back of the head also starts to thin and fall out. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, LLLT, and hair transplantation.
- Norwood Stage 7: Complete baldness. Treatment options include hair transplantation and scalp micro-pigmentation.
Women
- Ludwig Stage 1: There is little or no hair loss. Treatment is usually not necessary at this stage.
- Ludwig Stage 2: There is a widening of the part in the hair, with some thinning of hair on the crown. Treatment options include topical minoxidil and LLLT.
- Ludwig Stage 3: The hair on the crown becomes more noticeably thin. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, LLLT, and hair transplantation.
- Ludwig Stage 4: The hair on the crown becomes very thin, and there may be some hair loss at the temples. Treatment options include topical minoxidil, LLLT, and hair transplantation.
- Ludwig Stage 5: The crown is almost completely bald. Treatment options include hair transplantation and scalp micro-pigmentation.
It is important to note that these are just general treatment guidelines. The best treatment option for you will depend on your individual case and stage of hair loss.
Case studies
Case report 1
A 35-year-old man presented to his doctor with a 5-year history of progressive hair loss. He had noticed that his hairline had receded and that he was losing hair on the crown of his head. He was concerned about his hair loss and wanted to know what could be done to help.
The doctor examined the man's scalp and found that he had classic signs of AGA. The man's hairline had receded about 2 inches, and he had thinning hair on the crown of his head. The doctor also ordered blood tests to rule out other possible causes of hair loss. The blood tests were normal.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor diagnosed the man with AGA and recommended that he start treatment with minoxidil. The man agreed to start treatment, and he was seen back in 6 months. At the 6-month follow-up visit, the man reported that he was pleased with the results of the treatment. He said that he had noticed new hair growth in the areas where he had been applying the minoxidil.
Case report 2
A 45-year-old woman presented to her doctor with a 10-year history of progressive hair loss. She had noticed that her hair was becoming thinner and that she was losing more hair than usual when she shampooed or combed her hair. She was concerned about her hair loss and wanted to know what could be done to help.
The doctor examined the woman's scalp and found that she had classic signs of AGA. The woman's hair was thinning all over her scalp, but it was most noticeable at the temples and crown. The doctor also ordered blood tests to rule out other possible causes of hair loss. The blood tests were normal.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor diagnosed the woman with AGA and recommended that she start treatment with finasteride. The woman agreed to start treatment, and she was seen back in 6 months. At the 6-month follow-up visit, the woman reported that she was pleased with the results of the treatment.
Disclaimer- The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of M3 India.
About the author of this article: Dr Monica Gundecha is an MD (skin & VD) from Pune.
-
Exclusive Write-ups & Webinars by KOLs
-
Daily Quiz by specialty
-
Paid Market Research Surveys
-
Case discussions, News & Journals' summaries